Quizzes > High School Quizzes > Science
Coxal Bone Practice Quiz Challenge
Enhance bone anatomy mastery with engaging practice.

Study Outcomes
- Identify key anatomical landmarks of the coxal bone.
- Label major regions of the hip bone on diagrams.
- Understand the structural relationships between coxal bone features.
- Analyze the functional significance of coxal bone landmarks in hip movement.
- Apply anatomical knowledge to answer quiz questions effectively.
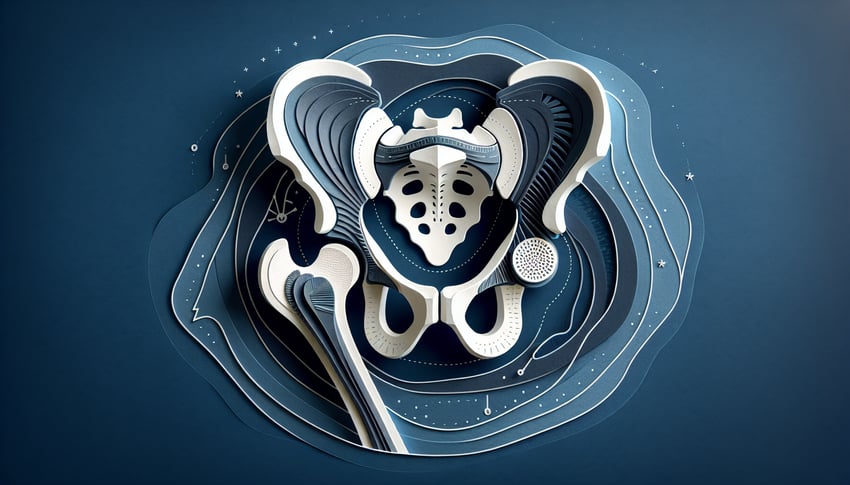
Coxal Bone Quiz - Anatomy Review Cheat Sheet
- Coxal Bone Fusion - The coxal bone, or hip bone, is actually three bones (ilium, ischium, pubis) elegantly fused together at the acetabulum. This fusion creates a sturdy basin for the hip joint, letting you kick, run, and dance. kenhub hip bone Kenhub Article
- Ilium & Iliac Crest - The ilium is the largest part of the hip bone, crowned by the iliac crest, which you can feel just under your hands when you place them on your waist. It serves as an anchor for core and thigh muscles, making it a hotspot for strength and stability. getbodysmart hip bone intro GetBodySmart Overview
- Ischium & Ischial Tuberosity - The ischium makes up the lower back portion of the hip bone, featuring the ischial tuberosity ("sit bone") that bears your weight when you park yourself on a chair. It also anchors your powerful hamstring muscles for sprinting and leaping. kenhub hip bone Kenhub Article
- Pubis & Pubic Symphysis - The pubis is the front piece of the hip bone, meeting its partner at the pubic symphysis - a slightly movable joint cushioned by cartilage. This gives just enough flexibility to help you walk smoothly and absorb shocks. getbodysmart hip bone intro GetBodySmart Overview
- Acetabulum Socket - The acetabulum is the deep, cup-shaped socket where the head of the femur nests, forming the classic ball-and-socket hip joint. Its snug fit provides both stability for weight-bearing and freedom for a wide range of motion. en.wikipedia acetabulum Wikipedia: Acetabulum
- Obturator Foramen - The obturator foramen is a large opening forged by the ischium and pubis, creating a gateway for nerves and vessels to travel into your legs. A thin membrane covers most of it, making this passage super-efficient yet protected. kenhub hip bone Kenhub Article
- Greater Sciatic Notch - Nestled between the ilium and ischium, the greater sciatic notch transforms into a foramen by ligaments, letting the sciatic nerve - the body's longest nerve - glide down to your thigh. It's a key corridor for nerve traffic control. getbodysmart hip bone intro GetBodySmart Overview
- Ischiofemoral Ligament - This strong band wraps around the back of the hip joint, limiting excessive internal rotation and adduction when your hip is flexed. It's one of the superheroes keeping your hip from over-rotating. en.wikipedia ischiofemoral ligament Wikipedia: Ischiofemoral Ligament
- Iliac Crest Landmark - Stretching from the anterior to posterior superior iliac spines, the iliac crest is a prime real estate for muscle attachments - from your abs to lower back. It's also a go-to surface landmark for clinicians and bodybuilders alike. getbodysmart hip bone intro GetBodySmart Overview
- Ischial Spine - The ischial spine is a sharp projection from the ischium, acting as a pulley point for the sacrospinous ligament. You'll find it sandwiched between the greater and lesser sciatic notches. kenhub hip bone Kenhub Article