Ready to Master Chapter 11 Properties of the Hair & Scalp? Take the Quiz!
Tackle Milady Chapter 11 review questions! Discover if you know why extremely curly hair does not typically retain moisture and master your workbook answers.
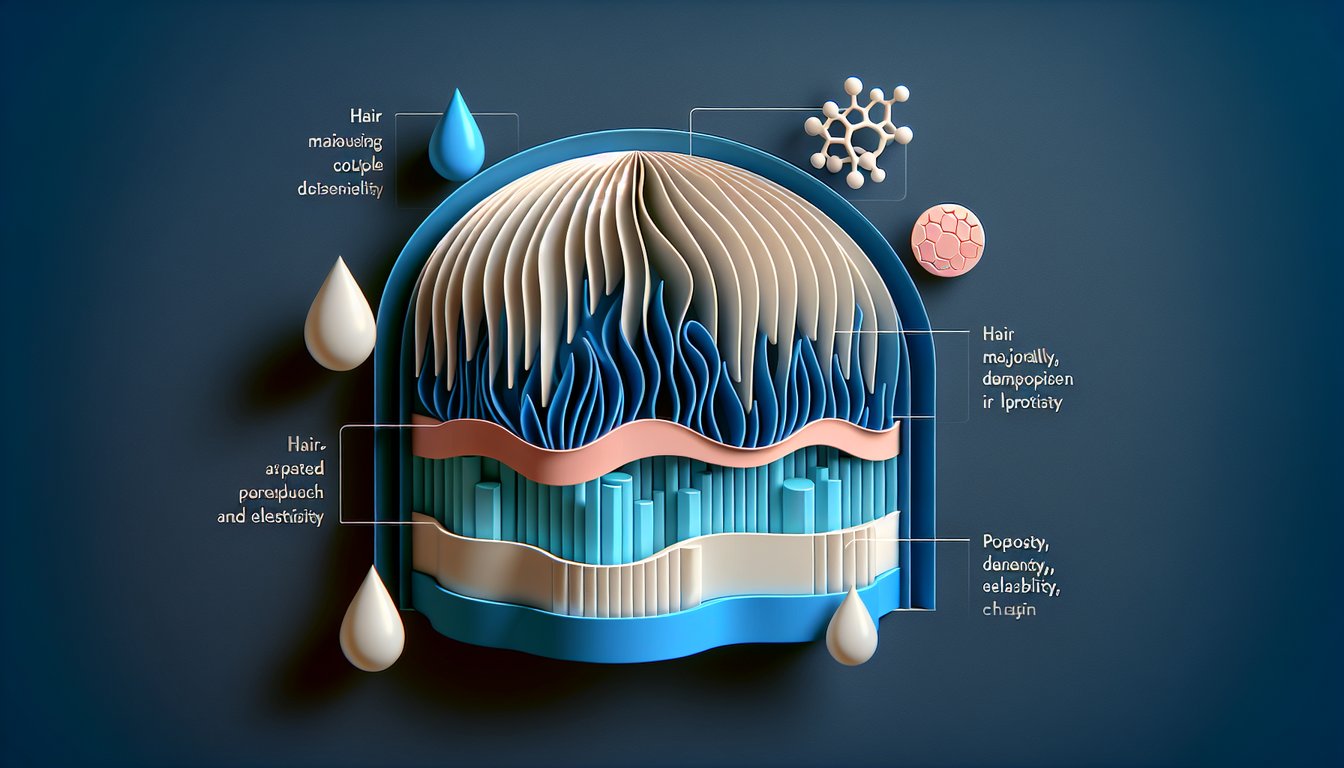
Calling all future stylists and beauty pros! Ready to master the chapter 11 properties of the hair and scalp? Our free Hair & Scalp Properties quiz puts you to the test with chapter 11 review questions milady - discover why hair is approximately 90 percent protein and how porosity, density and elasticity define every strand. Explore trichoptilosis, living cells that form the hair strand, and why extremely curly hair does not typically behave like straight or wavy textures. Whether you're hunting milady chapter 11 workbook answers or brushing up before class, this quick challenge sharpens your skills and boosts your confidence. Get instant feedback and see where you stand. Dive in and start conquering your cosmetology goals now with our hair porosity quiz!
Study Outcomes
- Understand the Protein Structure of Hair -
Explain why hair is approximately 90 percent protein and how this composition affects strength and resilience.
- Analyze Hair Porosity Levels -
Differentiate between high, medium, and low porosity and determine how porosity influences product absorption and styling outcomes.
- Evaluate Hair Density Classifications -
Assess the methods for measuring hair density and recognize the impact of density on volume and styling techniques.
- Assess Hair Elasticity Properties -
Identify the factors that contribute to elasticity and predict how elasticity variations affect hair stretch and breakage.
- Identify Characteristics of Extremely Curly Hair -
Recognize the unique structural properties of extremely curly hair and apply appropriate care strategies for this hair type.
- Apply Milady Chapter 11 Review Questions -
Use milady chapter 11 workbook answers and chapter 11 review questions milady to reinforce key concepts and prepare for practical exams.
Cheat Sheet
- Keratin-Based Composition -
Hair is approximately 90 percent protein, mainly keratin, as outlined in dermatology research from institutions like Johns Hopkins University. This fibrous protein provides tensile strength and resilience, supporting overall hair health. Use the mnemonic "K-PED" (Keratin, Porosity, Elasticity, Density) to recall the primary properties for Chapter 11 review questions Milady.
- Porosity Levels -
Porosity describes the hair's ability to absorb and retain moisture, categorized as low, normal, or high, a concept emphasized in Milady Chapter 11 workbook answers. A simple float test - placing a strand in water - helps gauge porosity: low floats, high sinks. Remember "S.H.O.C." (Slick cuticle, High absorption, Open cuticle, Capillary action) to identify high porosity quickly.
- Hair Density Measurement -
A concept covered in Chapter 11 Properties of the Hair and Scalp, density refers to the number of active hair follicles per square inch, influencing volume and styling approaches; average density is about 2,200 follicles per inch². You can estimate density by parting a one-inch square section and counting strands, then compare to Milady standards. High-density hair offers more styling fullness but requires more product, so adjust formulas accordingly.
- Elasticity and Stretch Ratio -
Elasticity measures hair's ability to return to its original length after stretching, calculated by ((stretched length − original length)/original length)×100. Dry hair typically stretches 20%, while wet hair can reach 50%, as supported by Journal of Cosmetic Science studies. Testing elasticity regularly helps prevent breakage by identifying when deep conditioning is needed.
- Curvature and Extreme Curl -
Extremely curly hair does not typically lie flat due to its tight coil pattern and elliptical follicle shape, which also makes moisture retention more challenging. According to research from the University of Texas Dermatology Department, this curl type has more cuticle layers, increasing porosity and dryness. Use a hydrating leave-in and wide-tooth comb to define coils and reduce frizz.







