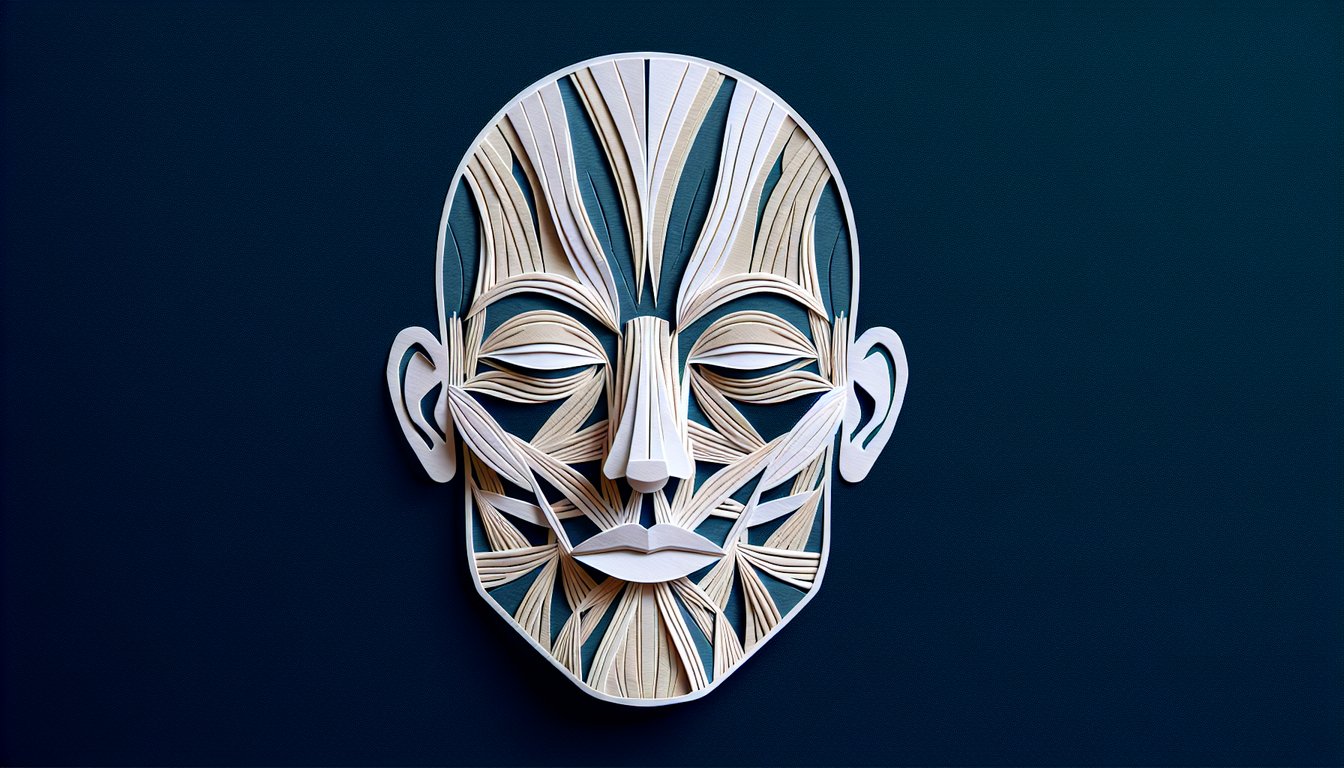
Label Face Muscles: Practice Quiz
Test your skills with comprehensive muscle labeling quiz

Study Outcomes
- Understand the anatomical location and function of key facial muscles.
- Identify facial muscles on diagrams and labeled images.
- Apply knowledge of muscle structure to interpret facial expressions.
- Analyze the relationship between muscle activity and facial movements.
- Evaluate differences among various facial muscle groups.
Label the Muscles Quiz - Face & Body Cheat Sheet
- Facial Muscles Overview - Dive into the gang of about 20 flat skeletal muscles lurking beneath your skin and scalp, all working together to help you smirk, pout, and express every emotion under the sun. These muscles are the real MVPs of nonverbal communication, giving your face its superpower. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Muscle Group Breakdown - The facial muscles aren't a random jumble; they're organized into neat squads like the mouth team, nose squad, cranium and neck crew, external ear ensemble, and eyelid unit. Each one has its own specialty, from wiggling ears to raising eyebrows. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Orbicularis Oculi - This circular muscle hugs your eye socket and is your built‑in blink factory, protecting and moisturizing your corneas. Next time you wink, thank the orbicularis oculi for that smooth action. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Orbicularis Oris - Surrounding your mouth like a stylish belt, this muscle puckers your lips for kisses, plays a starring role in whistling, and helps you articulate words. It's the pout engineer you never knew you needed. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Buccinator - Hidden deep in your cheek, the buccinator compresses your cheeks against your teeth so you can chew like a champ and avoid cheekfuls of food pooling in your mouth. It's the unsung hero of mealtime efficiency. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Zygomaticus Major - When you flash a genuine smile, it's this muscle pulling the corners of your mouth skyward. It's basically your built‑in happiness booster - no assembly required. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Depressor Anguli Oris - Feeling blue or about to deliver a dramatic performance? This muscle drags the corners of your mouth downward, giving your face that classic frown or sad vibe. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Frontalis - Surprise! Blame it on the frontalis, the muscle that raises your eyebrows and wrinkles your forehead in one smooth move. It's your go‑to for those "Wait, what?!" moments. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Platysma - Stretching from your jaw down to your collarbone, this muscle tenses the skin of your neck and can help drop your lower jaw. It's perfect for conveying tension or that "I'm concentrating hard" look. Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide
- Facial Nerve (VII) - The mastermind behind all those movements, cranial nerve VII innervates every facial expression muscle, ensuring your smile, sneer, or sleepy blink happens on cue. Damage here and the show stops! Kenhub - Facial Muscles Guide